How Quantum Computing works – A Step-by-step Guide
How Quantum Computing works – A Step-by-step Guide
Welcome to the mind-bending world of quantum computing! While traditional computers operate on binary digits, or bits, which can only exist in one state at a time (either 0 or 1), quantum computers leverage the principles of quantum mechanics to process information using qubits that can exist in multiple states simultaneously. This revolutionary technology promises immense computational power and could potentially solve problems that are beyond the capabilities of classical computing.
In this step-by-step guide, we'll explore how quantum computing works, its benefits and drawbacks, and what the future holds for this exciting field. So fasten your seatbelts as we embark on an exhilarating journey into the realm of quantum computing!
What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing is a type of computing that uses the principles of quantum physics to perform calculations. Unlike classical computers, which use bits (zeros and ones) as the basic units of information, quantum computers use qubits (quantum bits), which can exist in multiple states at once.
This allows quantum computers to perform certain types of calculations much faster than classical computers. For example, they could be used to factor large numbers or simulate complex chemical reactions.
One key feature of quantum computing is superposition. This means that a qubit can exist in multiple states simultaneously until it is measured. Another key feature is entanglement, where two qubits become correlated with each other even when separated by large distances.
While still in its early stages, research into quantum computing has already yielded promising results and potential applications for fields such as cryptography and drug discovery. However, there are also challenges to overcome such as maintaining the delicate state of qubits during computation.
How Does Quantum Computing Work?
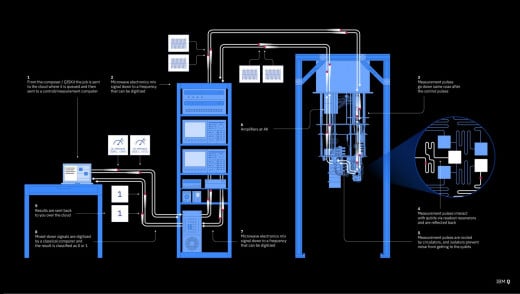
Quantum computing is a fascinating field that explores the principles of quantum mechanics to process information. In conventional computers, we use bits (0s and 1s) as the basic unit of data processing. However, in quantum computing, we use qubits that can represent both states at once.
These qubits can be manipulated by applying operations such as superposition and entanglement, which allows for parallel computation. This means that quantum computers can perform certain tasks exponentially faster than their classical counterparts.
In simple terms, if you have a problem with many possible solutions like factorizing large numbers or searching through vast databases, a quantum computer could find the solution much faster than traditional computers. Though this kind of processing power has potential applications in various fields like medicine or finance but it's still under development.
While there are challenges to building practical quantum computers such as maintaining coherence between qubits and minimizing errors during computation due to environmental noise factors; however significant progress has already been made in developing reliable ways of manipulating these elusive particles called qubits.
Quantum computing is an exciting area full of possibilities for advancing science and technology in numerous fields from cryptography to logistics optimization.
The Benefits of Quantum Computing
Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize various industries by solving complex problems faster than traditional computers. Here are some of the benefits that quantum computing offers:
- Faster Problem-Solving: Quantum computers can solve problems exponentially faster than classical computers, making them ideal for tasks such as cryptography and simulation.
- Improved Data Analysis: With quantum computing's ability to process vast amounts of data at once, it could provide more accurate insights in fields like finance and medicine.
- Better Optimization: Quantum computing algorithms can optimize complex systems better than classical algorithms, which would be useful in areas like logistics and transportation planning.
- Enhanced Machine Learning: Quantum machine learning models could improve AI capabilities by providing more efficient training methods and better decision-making processes.
- Advancements in Material Science: By simulating molecular structures with greater accuracy, quantum computers could help identify new materials with unique properties for use in various applications.
While still in its early stages of development, quantum computing holds immense promise for transforming many aspects of our lives through faster problem-solving, improved data analysis and optimization techniques among others!
The Drawbacks of Quantum Computing
While the potential benefits of quantum computing are vast, there are also some significant drawbacks to consider. One of the main challenges is that quantum computers are incredibly complex and difficult to build, which makes them expensive and not scalable for widespread use.
Another issue is that quantum algorithms can be highly sensitive to errors, meaning that even small mistakes in calculations can have a significant impact on results. This could limit their usefulness in certain applications where precision is critical.
Moreover, current quantum computers still have limited processing power compared to traditional computers, making them unsuitable for many practical tasks at present. Additionally, there are concerns about the security implications of this technology as it may potentially render many encryption techniques obsolete.
It's worth considering whether investing heavily in advancing this technology will ultimately pay off since it remains unclear which industries or fields could benefit most from its development.
While there's no denying the exciting possibilities offered by quantum computing research today - we must also remain aware of these limitations if we're hoping for realistic expectations moving forward.
The Future of Quantum Computing
The future of quantum computing is both exciting and uncertain. Quantum computers have the potential to revolutionize industries such as finance, healthcare, and cybersecurity. With their ability to solve complex problems much faster than classical computers, they could lead to major breakthroughs in fields like drug discovery and climate modeling.
However, there are still many challenges to overcome before quantum computers become widely available. One major hurdle is the issue of error correction - quantum systems are extremely sensitive and prone to errors, which can quickly accumulate during a computation.
Despite these difficulties, researchers around the world are working hard to develop practical applications for quantum computing. Major tech companies like IBM and Google have built prototype machines with dozens or even hundreds of qubits (the basic unit of information in a quantum computer), while startups like Rigetti Computing are developing cloud-based platforms for users to experiment with quantum algorithms.
It's clear that we're only scratching the surface when it comes to what's possible with this revolutionary technology. The full potential of quantum computing may not be realized for decades or even centuries - but one thing is certain: it will continue pushing the boundaries of our understanding of physics and computation well into the future.
As we have seen in this step-by-step guide, quantum computing works by utilizing the principles of superposition and entanglement. These principles allow for qubits to represent multiple states simultaneously, increasing computational power exponentially.
The benefits of quantum computing include faster processing times, increased efficiency, and improved accuracy. However, there are also drawbacks such as high costs and technical limitations.
Despite these challenges, the future of quantum computing looks bright. With advancements being made every day in research labs around the world, we can expect to see more practical applications for this technology in areas like medicine, finance, cryptography and much more.
Quantum Computing will change how we approach problem-solving forever - enabling us not only solve current problems but uncover new ones too!


Comments
Post a Comment